From Snail Slime to Royal Robes: The Gruesome Price of Ancient Purple Dye
For centuries, Tyrian purple was a color reserved for emperors and kings. Discover the startling reason why producing this legendary dye required crushing thousands upon thousands of sea snails.


Too Long; Didn't Read
The prestigious and expensive Tyrian purple dye was historically made by crushing thousands of specific sea snails to produce even a small amount, making it a symbol of immense wealth and power.
From Snail Slime to Royal Robes: Why Did Making Purple Dye Historically Require Crushing Thousands of Sea Snails?
Imagine a color so rare, so vibrant, and so enduring that it became synonymous with emperors, kings, and immense wealth. For centuries, Tyrian purple held this prestigious position. But behind its regal allure lies a startling fact: producing even a small amount of this legendary dye required the sacrifice of thousands upon thousands of specific sea snails. Why was such a seemingly gruesome and labor-intensive process necessary? This post delves into the fascinating history and science behind the ancient world's most coveted color.
The Quest for Purple: A Color Reserved for Royalty
Long before synthetic dyes offered a rainbow of affordable options, vibrant colors were notoriously difficult and expensive to produce. Among the most prized was Tyrian purple, named after the Phoenician city of Tyre, a major center of its production. Its association with power was profound; Roman senators wore togas with a purple stripe, emperors donned entirely purple garments, and laws often restricted its use to the ruling elite. This exclusivity wasn't just arbitrary; it stemmed directly from the extreme difficulty and cost of its creation.
The Source: Not Just Any Snail
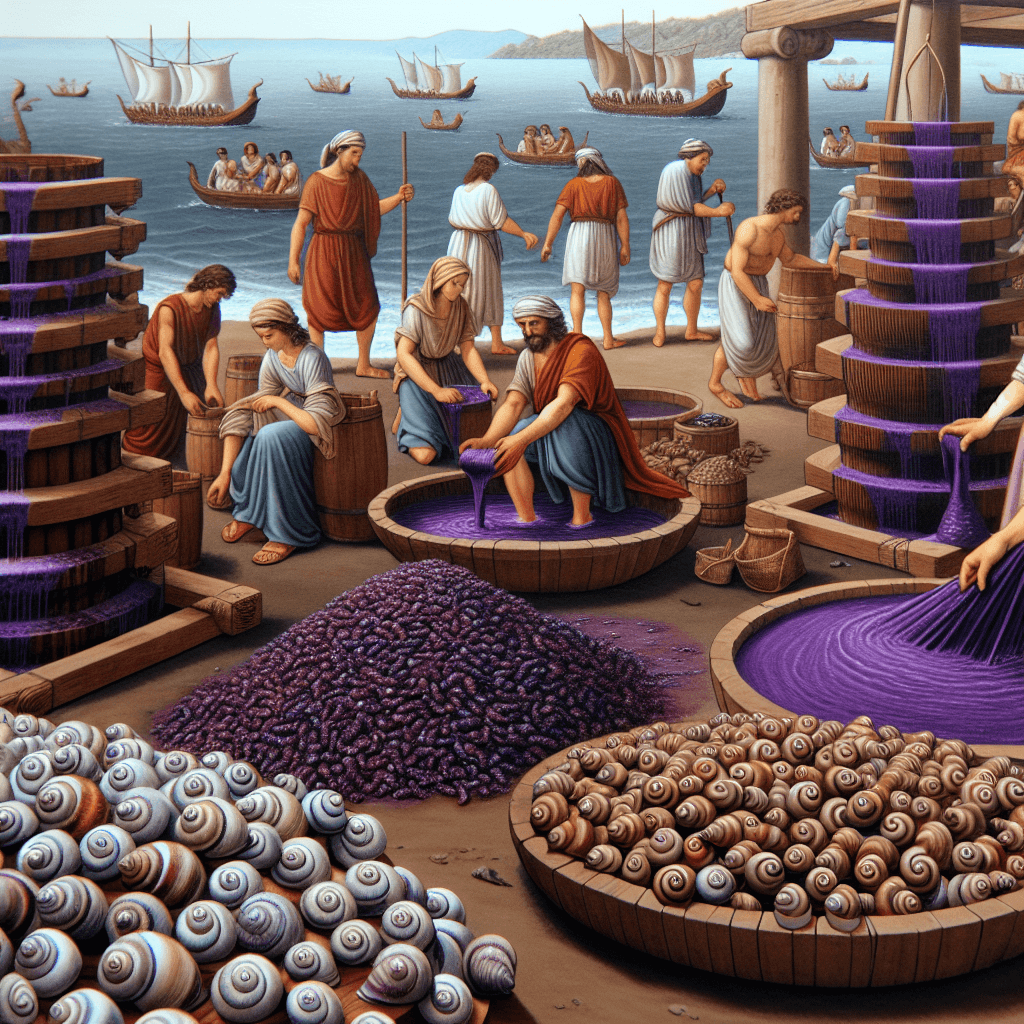
The key ingredient for Tyrian purple wasn't easily found. It came from the hypobranchial gland of several species of predatory sea snails, primarily found in the Mediterranean Sea. The most commonly cited species include:
- Bolinus brandaris (originally Murex brandaris)
- Hexaplex trunculus
- Stramonita haemastoma
These snails weren't farmed; they had to be painstakingly harvested from the sea, often by hand or using bait traps. Archaeological evidence, including massive mounds of discarded shells near ancient production sites, attests to the scale of this operation.
The Tiny Yield: The Crux of the Problem
Here lies the core reason why so many snails were needed: each individual snail contains only a minuscule amount of the necessary dye precursor.
Historical accounts and modern reconstructions estimate that it took anywhere from 10,000 to 12,000 snails to produce just 1 to 1.4 grams of pure Tyrian purple dye. That's barely enough to dye the trim on a single garment, let alone a full robe!
Think about the logistics:
- Harvesting: Locating and collecting tens of thousands of these specific snails from the sea floor.
- Extraction: Carefully extracting the tiny hypobranchial gland from each snail, or crushing them and extracting the fluid (a closely guarded, often unpleasant, process).
This immense labor requirement, combined with the sheer number of individual creatures needed, made the raw material incredibly precious.
The Complex Chemistry: From Clear Mucus to Vibrant Purple
The process didn't end with extraction. The clear or yellowish mucus secreted by the snail's gland wasn't purple initially. It contained precursors (like derivatives of indole) that needed to undergo a specific chemical transformation.
This typically involved:
- Exposure: Allowing the extracted fluid to react with sunlight and air.
- Transformation: A complex process involving enzymatic reactions and photo-oxidation turned the precursors into the final pigment, primarily 6,6'-dibromoindigo.
This process was often smelly and required skill and patience. Different snail species and variations in the process could yield slightly different shades, ranging from reddish-purple to a deeper violet. Crucially, the resulting dye was incredibly colorfast – resistant to fading from sunlight and washing – adding further to its value. It wasn't just purple; it was permanent purple.
Conclusion: A Legacy Dyed in Purple
The reason making Tyrian purple historically required crushing thousands of sea snails boils down to simple biology and complex chemistry: each snail offered only a tiny drop of potential color, locked within a gland that needed careful extraction and processing. The sheer volume of snails required for even a small yield drove the dye's immense cost and cemented its status as a symbol of ultimate luxury and power for millennia.
While modern chemistry has long since provided synthetic alternatives, the story of Tyrian purple serves as a potent reminder of the ingenuity and incredible effort our ancestors invested in harnessing the natural world, and the staggering price once paid for a color fit for kings.