Unmasking the Night Terrors: Why We Experience Sleep Paralysis with Vivid Hallucinations
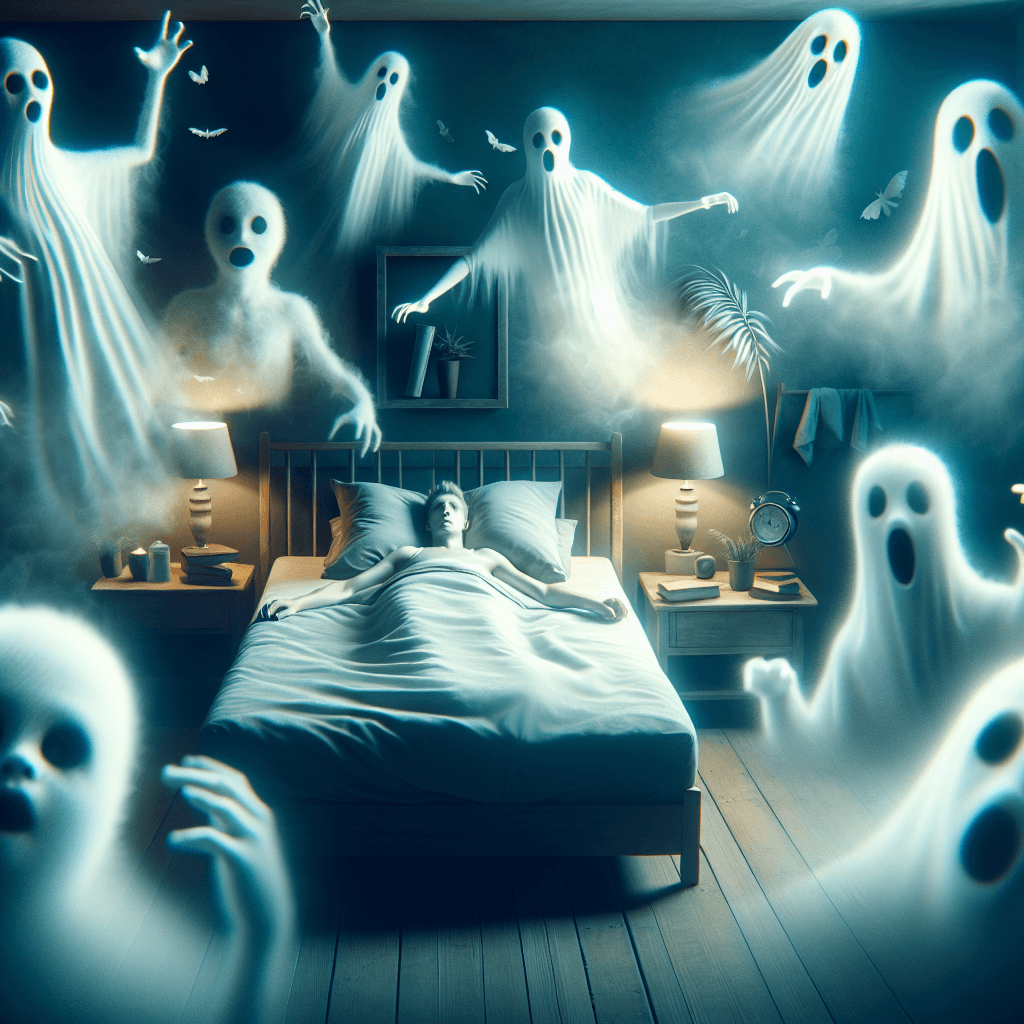
Ever woken up alert but completely frozen, perhaps sensing an ominous presence? This terrifying experience is known as sleep paralysis, and it's more common than you think.


Too Long; Didn't Read
Sleep paralysis is a common condition where your mind wakes up before your body, causing temporary paralysis and often leading to vivid, frightening hallucinations.
Unmasking the Night Terrors: Why Do We Sometimes Experience Sleep Paralysis with Vivid Hallucinations?
Have you ever woken up in the dead of night, your mind alert but your body completely frozen, perhaps sensing an ominous presence or seeing shadowy figures in your room? This terrifying experience, known as sleep paralysis accompanied by vivid hallucinations, is more common than you might think, affecting an estimated 8% of the general population at some point in their lives. While often deeply unsettling, understanding the science behind this phenomenon can help demystify it and reduce associated fear. This blog post will delve into the reasons why we sometimes experience sleep paralysis with vivid hallucinations, exploring the fascinating interplay between our sleep cycles and waking consciousness.
What Exactly is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak that occurs when you are falling asleep (hypnagogic state) or waking up (hypnopompic state). During these transitions, you are consciously aware of your surroundings, but your body remains temporarily immobilized. This paralysis is actually a natural and protective mechanism.
During Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, the stage where most vivid dreaming occurs, our brains send signals to essentially switch off voluntary muscles. This is called REM atonia, and it prevents us from physically acting out our dreams – imagine thrashing around or running while dreaming about being chased! Sleep paralysis happens when your brain wakes up before your body "catches up" and releases this muscle atonia. You become conscious, but the paralysis lingers for a few seconds to a few minutes.
The Mystery of the Hallucinations: Why Do They Occur?
The truly frightening aspect for many is not just the paralysis but the accompanying vivid and often terrifying hallucinations. These aren't typical dreams; they feel intensely real because you are, in fact, partially awake. These hallucinations can be:
- Intruder Hallucinations: The most common type, involving a sense of a threatening presence, hearing footsteps or voices, or seeing figures like shadows or "demons" in the room.
- Incubus/Chest Pressure Hallucinations: Characterized by a feeling of pressure on the chest, difficulty breathing, or a sensation of being choked or suffocated, often attributed to a malevolent entity.
- Vestibular-Motor (Out-of-Body) Hallucinations: Less common, these can involve sensations of floating, flying, spinning, or having an out-of-body experience.
These hallucinations are thought to occur because elements of REM sleep, particularly the dream imagery and emotional intensity, intrude into your waking consciousness. Your brain, trying to make sense of the paralysis and the lingering dream-like state, can conjure these frightening scenarios.
The Brain's Role: A Mismatch in Consciousness
The core reason we experience sleep paralysis with hallucinations lies in a "glitch" in the sleep-wake transition. Essentially, your mind wakes up while your body is still in the REM sleep state.
REM Intrusion
Sleep researchers believe that sleep paralysis is a mixed state of consciousness where features of REM sleep persist into wakefulness. While your awareness returns, your brain might still be partially "dreaming." The parts of your brain active during REM, like the amygdala (involved in processing fear and emotion), are still highly active. This can explain the intense fear and the threatening nature of many hallucinations. Your brain tries to interpret the unusual signals – the paralysis and the dream-like imagery – and often defaults to fear-based explanations.
For instance, the sensation of pressure on the chest (incubus hallucination) might be the brain's interpretation of normal changes in breathing patterns during REM sleep combined with the fear generated by the paralysis itself.
Contributing Factors and Triggers
While anyone can experience sleep paralysis, certain factors can increase its likelihood:
- Sleep Deprivation: Not getting enough sleep is a primary trigger.
- Irregular Sleep Schedules: Shift work or inconsistent bedtimes can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle.
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress or anxiety disorders can make episodes more frequent.
- Sleeping Position: Many report episodes occurring more frequently when sleeping on their back (supine position).
- Certain Medical Conditions: Narcolepsy (a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks) is strongly linked to sleep paralysis.
- Mental Health Conditions: Conditions like PTSD and panic disorder have also been associated with an increased risk.
- Family History: There may be a genetic predisposition, as it sometimes runs in families.
Understanding these triggers can be a first step in potentially reducing the frequency of episodes.
Conclusion: Frightening, But Usually Harmless
Experiencing sleep paralysis with vivid hallucinations can be a profoundly disturbing event, often leaving individuals feeling shaken and fearful of sleep itself. However, it's crucial to remember that it is a common, naturally occurring phenomenon rooted in the complex mechanisms of our sleep cycles, specifically a temporary disconnect between brain and body during the transition from REM sleep. The hallucinations, while feeling incredibly real, are essentially dream elements spilling over into a state of partial wakefulness.
While typically harmless from a physical standpoint, understanding why sleep paralysis and its accompanying visions occur can significantly alleviate the fear associated with them. If episodes are frequent or cause significant distress, consulting a healthcare professional can help rule out underlying conditions and explore management strategies. Knowledge, in this case, truly is power against the terrors of the night.